Introduction
With cities’ rapid expansion and increasing population density, urban mobility has become a critical concern for city planners, transportation authorities, and policymakers. The volume of data generated by public transport systems, ride-sharing services, GPS-enabled devices, and IoT sensors has grown exponentially. Processing, storing, and analysing this vast amount of data is crucial for optimising transportation networks, reducing congestion, and improving commuter experiences.
Hadoop and Spark, two powerful big data technologies, have emerged as the leading solutions for managing massive urban mobility datasets. These frameworks enable real-time data processing, large-scale analytics, and predictive modelling to support smart city initiatives. Professionals looking to master these technologies can benefit from a Data Science Course, which provides hands-on experience in big data processing and analytics.
The Need for Big Data in Urban Mobility
Traditional methods of transportation data analysis are no longer sufficient to handle the velocity, volume, and variety of urban mobility data. Cities generate data from multiple sources, including:
- Public Transport Systems: Real-time data from buses, trains, and metros.
- Ride-sharing & Taxi Services: Trip data from Uber, Lyft, and similar platforms.
- Traffic Sensors & Cameras: IoT-enabled road surveillance and congestion tracking.
- GPS & Mobile Applications: Location data from smartphones and navigation apps.
- Weather & Environmental Sensors: Data affecting road conditions and travel patterns.
Managing and analysing these datasets requires distributed computing frameworks like Hadoop and Apache Spark, which can efficiently process large-scale mobility data. A Data Science Course can teach professionals how to leverage these tools to extract meaningful insights from massive datasets.
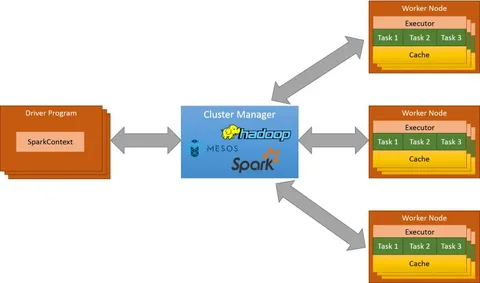
Hadoop for Managing Urban Mobility Data
Hadoop is an open-source framework that can store and process big data across distributed clusters of computers. It is well-suited for handling massive urban mobility datasets.
Key Advantages of Hadoop for Urban Mobility Data:
Scalability
Hadoop’s HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) enables data storage across multiple nodes, making it highly scalable.
As cities generate petabytes of mobility data, Hadoop can store and process it efficiently.
Fault Tolerance
Urban data is continuously generated, and Hadoop ensures data reliability by replicating data across multiple nodes to prevent data loss.
Cost-Effectiveness
Hadoop runs on commodity hardware, making it a cost-effective solution for large-scale data storage and processing. Enrolling in a Data Science Course in Bangalore and such cities can help professionals develop the skills necessary to design cost-effective models for storing and processing data using Hadoop.
Batch Processing Capabilities
MapReduce, Hadoop’s processing model, enables batch processing of urban mobility data for historical analysis, route optimisation, and congestion prediction.
Apache Spark for Real-Time Urban Mobility Analytics
While Hadoop is excellent for batch processing, it struggles with real-time analytics. This is where Apache Spark comes in. Spark is a distributed computing framework that processes large datasets 100x faster than Hadoop’s MapReduce due to its in-memory computation capabilities.
Key Advantages of Spark for Urban Mobility Data:
Real-Time Data Processing
Spark Streaming allows real-time mobility data processing, making it ideal for predictive traffic modelling, live traffic monitoring, and anomaly detection in transportation systems.
Faster Computation with In-Memory Processing
Unlike Hadoop’s disk-based processing, Spark stores data in memory, reducing latency and speeding up analytics.
Advanced Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
Spark integrates MLlib, a powerful machine learning library, for:
- Predicting travel demand in ride-sharing services.
- Optimising public transport schedules based on commuter trends.
- Detecting traffic incidents using anomaly detection techniques.
A Data Science Course can provide hands-on experience in developing such machine learning models with Spark MLlib.
Interactive Data Analysis
Spark SQL allows for efficient querying of massive mobility datasets, making it easy for data scientists and analysts to extract insights.
Hadoop vs. Spark for Urban Mobility Data
| Feature | Hadoop | Spark |
| Processing type | Batch Processing | Real-time and Batch Processing |
| Speed | Slower due to disk-based processing | 100x faster with in-memory computation |
| Fault Tolerance | High, with data replication | High, with DAG-based execution |
| Scalability | Scales horizontally with commodity hardware | Scales well but requires more memory |
| Machine Learning | Limited support | Built-in MLlib for predictive analytics |
| Best Use Case | Long-term data storage and historical analysis | Real-time analytics and predictive modelling |
Both Hadoop and Spark complement each other, making them powerful tools for end-to-end mobility data management.
Challenges in Managing Urban Mobility Data
Despite the advantages of Hadoop and Spark, managing massive urban mobility datasets comes with challenges:
Data Integration Complexity
Mobility data is heterogeneous, coming from GPS, IoT sensors, social media, and transport databases. Integrating these diverse datasets requires ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines.
High Infrastructure Costs
While Hadoop and Spark reduce storage and processing costs, maintaining a distributed computing cluster requires significant infrastructure investment.
Data Security & Privacy Concerns
Real-time tracking and personal mobility data raise concerns about user privacy and cybersecurity risks. Encryption and access control mechanisms need to be implemented.
Understanding these challenges and learning solutions is the focus in any career-oriented data course, such as a Data Science Course in Bangalore, where professionals are oriented to gain expertise in data governance and security in big data environments.
Real-World Applications of Hadoop & Spark in Urban Mobility
- Smart Traffic Management (New York City) – Uses Hadoop & Spark to optimise traffic flow.
- Public Transport Optimisation (Singapore) – Analyses commuter trends for better scheduling.
- Ride-sharing optimisation (Uber & Lyft) – Uses Spark Streaming to improve driver-passenger matching.
- Air Pollution & Mobility Correlation (London) – Monitors real-time pollution levels.
Learning how to apply these technologies to address real-world issues is a key focus of a Data Science Course, enabling professionals to develop and deploy large-scale urban mobility solutions.
The Future of Big Data in Urban Mobility
- AI-Powered Autonomous Traffic Systems – Optimising traffic with machine learning.
- Blockchain for Secure Mobility Data Sharing – Secure and transparent transport data.
- Edge Computing for Faster Decision Making – Processing data closer to IoT devices.
With advancements in big data analytics, AI, and IoT, the demand for data science professionals skilled in Hadoop and Spark is growing. A Data Science Course can help individuals develop expertise in smart city projects and urban mobility analytics.
Conclusion
Managing massive urban mobility datasets requires scalable and efficient big data solutions. Hadoop is best suited for storing and batch-processing large-scale transport data, while Apache Spark excels in real-time analytics and predictive modelling. They empower smart cities to optimise traffic management, ride-sharing services, and public transport networks.
A well-rounded data program, such as a Data Science Course in Bangalore and such cities reputed for technical learning, can equip professionals with the necessary skills to work with Hadoop and Spark, helping cities make data-driven decisions for improved urban mobility.
ExcelR – Data Science, Data Analytics Course Training in Bangalore
Address: 49, 1st Cross, 27th Main, behind Tata Motors, 1st Stage, BTM Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560068
Phone: 096321 56744